Project Management
Earned Value- Project Management
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the purpose of Eearned Value Management in assessing project performance.
- Define and explain key terms in EVM, such as Planned Value (PV), Earned Value (EV), and Actual Cost (AC).
- Differentiate between terms like Budget at Completion (BAC) and Estimate at Completion (EAC).
Earned Value Basic Performance Metrics:
Cost Variance : Difference between projected cost and actual cost. \[CV = EV - AC\]
Schedule Variance : Difference between projected schedule and actual schedule. \[SV = EV - PV\]
Schedule Performance Index : A measure of how close the project is to performing work as it was actually scheduled. \[SPI = \dfrac{EV}{PV}\]
Cost Performance Index :A measure of how close the project is to spend on the work performed to what was planned to have been spent. \[CPI = \dfrac{EV}{AC}\]
Solved Example: 9011-01
Earned value management introduces a method to answer how much has been:
A. Left
B. Assigned
C. Accomplished
D. Projected
Correct Answer: C
WBS
Learning Objectives:
- Develop skills in creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to break down project scope into manageable work packages for EVM tracking.
- Dividing complex projects to simpler and manageable tasks is the process identified as Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
- Usually, the project managers use this method for simplifying the project execution. In WBS, much larger tasks are broken-down to manageable chunks of work. These chunks can be easily supervised and estimated.
- A work breakdown structure In project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable oriented decomposition of a project into smaller components.
- A work breakdown structure element may be a product, data, a service, or any combination. A WBS also provides the necessary framework for detailed cost estimating and control along with providing guidance for schedule development and control.
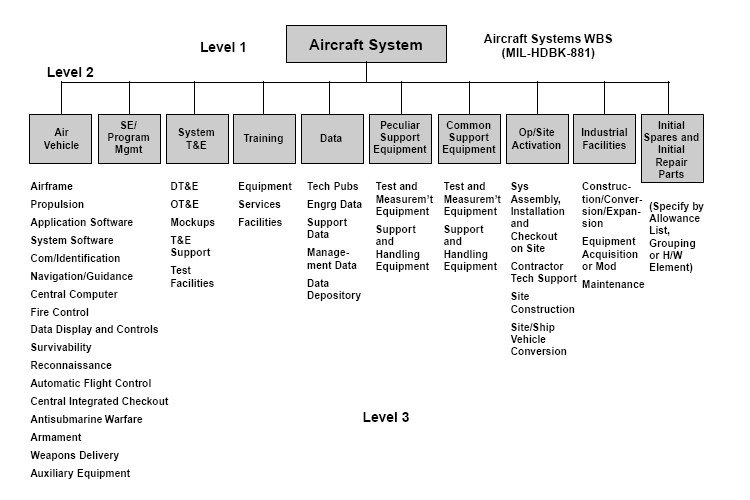
US gov, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Solved Example: 9008-01
Which one of the following is captured in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
A. The life cycle phases
B. The logical order of tasks
C. The scope of the project
D. Project costs
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9008-02
In a work-breakdown structure, the _________ approach to planning is adopted.
A. Bottom-up
B. Horizontal
C. Top-down
D. De-centralised
Correct Answer: C
PERT
Learning Objectives:
- Define PERT as a project management tool used to analyze and schedule the tasks involved in completing a project.
- Understand the principles and objectives of PERT in optimizing project timelines, resource allocation, and risk management.
- Familiarize with key components and terminology used in PERT, including nodes, activities, predecessors, successors, event times, and critical path.
- Understand the network representation of project activities and dependencies in PERT diagrams.
- Identify the specific activities and milestones.
- The activities are the tasks required to complete a project. The milestones are the events marking the beginning and the end of one or more activities.
- Determine the proper sequence of the activities. This step may be combined with the activity identification step since the activity sequence is evident for some tasks. Other tasks may require more analysis to determine the exact order in which they must be performed.
- Construct a network diagram. Using the activity sequence information, a network diagram can be drawn showing the sequence of the serial and parallel activities. Software packages simplify this step by automatically converting tabular activity information into a network diagram.
- Determine the proper sequence of the activities.
- Construct a network diagram.
- Estimate the time required for each activity.
- Weeks are a commonly used unit of time for activity completion, but any consistent unit of time can be used. A distinguishing feature of PERT is its ability to deal with uncertainty in activity completion time.
- Determine the critical path.
- Update the PERT chart as the project progresses.
- Update the PERT chart as the project progresses. Make adjustments in the PERT chart as the project progresses. As the project unfolds, the estimated times can be replaced with actual times. In cases where there are delays, additional resources may be needed to stay on schedule and the PERT chart may be modified to reflect the new situation.
-
The critical path is determined by adding the times for the activities in each sequence and determining the longest path in the project. The critical path determines the total calendar time required for the project. If activities outside the critical path speed up or slow down (within limits), the total project time does not change.
hu:User:Illes, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Solved Example: 9010-01
Pessimistic time and optimistic time of completion of an activity are given as 10 days and 4 days respectively, the variance of the activity will be:
A. 1
B. 6
C. 12
D. 18
Correct Answer: A
Solved Example: 9010-02
In construction project planning, free float can affect which of the following?
A. Only that particular activity
B. Succeeding activity
C. Overall completion
D. Preceding activity
Correct Answer: D
Solved Example: 9010-03
A PERT network has 9 activities on its critical path. The standard deviation of each activity on the critical path is 3. The standard deviation of the critical path is:
A. 3
B. 9
C. 81
D. 27
Correct Answer: B
Solved Example: 9010-04
The time by which the activity completion time can be delayed without affecting the start of succeeding activities is known as:
A. Duration
B. Total float
C. Free float
D. Interfering float
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9010-05
Gantt chats are used for:
A. Forecasting sales
B. Production schedule
C. Scheduling and routing
D. Linear Programming
Correct Answer: B
Solved Example: 9010-06
A point which represents either starting or termination of activity is known as _______
A. Loop
B. Network
C. Event
D. Algorithm
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9010-07
Dangling phenomenon in a network diagram:
A. Should be increased to the maximum possible extent.
B. Should be avoided.
C. Should be encouraged.
D. Should be inserted compulsorily.
Correct Answer: B
Solved Example: 9010-08
In a network diagram, an activity having a dotted arrow between activities is often referred to as a/an ________ activity.
A. Failed
B. Risky
C. Important
D. Dummy
Correct Answer: D
Solved Example: 9010-09
Pessimistic time is:
A. The maximum time which an activity might require
B. The average time required for a job
C. The most probable time considering all conditions
D. The minimum time in which an activity can possibly be accomplished
Correct Answer: A
Solved Example: 9010-10
The start or completion of task is called:
A. An event
B. An activity
C. A duration
D. None of these
Correct Answer: A
CPM
Learning Objectives:
- Familiarize with key components and terminology used in CPM, including activities, durations, predecessors, successors, early start, early finish, late start, late finish, and total float.
- Understand the network representation of project activities and dependencies in CPM diagrams.
- Learn how to calculate project timelines using forward pass and backward pass calculations in CPM.
- Understand how to determine the earliest start time (ES), earliest finish time (EF), latest start time (LS), latest finish time (LF), and total float (TF) for each activity in the network.
- Critical path refers to the longest path of a given project network
- Duration of a project is given by the length of the critical path
- Activities on a critical path are called critical activities while remaining activities are non-critical
- A project can have more than one critical path as well
- Critical activities are so called because their timely completion is critical to the completion of the project in time
- Critical activities can not be delayed while non- critical activities have some cushion available.
where,
d$_{ij}$ = duration of activity (i, j)
CP = critical path (longest path)
T = duration of project
Petr Kopač, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Solved Example: 9009-01
Critical path method is good for:
A. Small project only
B. Large project only
C. Both small and large projects equally
D. Neither small nor large projects
Correct Answer: B
Solved Example: 9009-02
CPM method of network analysis is
- Ideally suited for linearly extending works
- Meant essentially for research and development activities.
- Activity-oriented
- Used for planning, scheduling and controlling purposes
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 3 and 4 only
D. 1 and 4 only
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9009-03
The particular task performance in CPM is known as:
A. Dummy
B. Event
C. Activity
D. Contract
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9009-04
Total float can be expressed as:
(a) latest start time - earliest start time
(b) latest finish time - earliest finish time
A. Both (a) and (b) are false
B. (a) is true but (b) is false
C. Both (a) and (b) are true
D. (a) is false but (b) is true
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9009-05
The critical path:
A. Is a path that operates from the starting node to the end node
B. Is a mixture of all paths
C. Is the longest path
D. Is the shortest path
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9009-06
A project has 6 activities (A to F) with respective activity durations 7, 5, 6, 6, 8, 4 days. The network has three paths A-B, C-D and E-F. All the activities can be crashed with the same crash cost per day. The number of activities that need to be crashed to reduce the project duration by 1 day is:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 6
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9009-07
When a project is crashed:
A. Both direct and indirect costs increase
B. Indirect costs increase, and direct costs decrease
C. Direct costs increase, and indirect costs decrease
D. cost are of no criterion
Correct Answer: C
Solved Example: 9009-08
In CPM, the cost slope is determined by:
A. Crash cost/Normal Cost
B. (Crash Cost - Normal cost)/ (Normal time - Crash time)
C. Normal Cost/Crash cost
D. (Normal cost - Crash cost)/ (Normal time - Crash time)
Correct Answer: B
Agile
Learning Objectives:
- Define the concept of Agile Project Management.
- Differentiate Agile methodologies from traditional project management approaches.
Traditional PM Approach
- Concentrates on thorough, upfront planning of the entire project.
- Requires a high degree of predictability to be effective.
- Relies on incremental, iterative development cycles to complete less-predictable projects.
- Is ideal for exploratory projects in which requirements need to be discovered and new technology tested.
- Focuses on active collaboration between the project team and customer representatives.
Solved Example: 9012-01
How is Agile planning different from the traditional approach to planning?
A. Agile planning is done only once
B. Agile planning is non iterative
C. Agile planning places emphasis on the plan
D. Agile planning places emphasis on planning and is iterative
Correct Answer: D
Solved Example: 9012-02
What is the unit of measurement that is used to measure the size of a user story for an Agile project?
A. Function points
B. Story points
C. Work breakdown points
D. Velocity points
Correct Answer: B
Solved Example: 9012-03
When forming an Agile project team it is BEST to use:
A. Generalized Specialists
B. Top management officials
C. Highly specialized developers
D. All of the above
Correct Answer: A